Self-Sovereign Identity
March 29th, 2019
DSR has been working in the area of Blockchain for some time now and we are honored to be involved in the development of Sovereign Identity. As a follow up on a recent Blockchain meetup we organized, we wanted to share information on revolutionary concept of Self-Sovereign Identity, a practical and real application of Blockchain technology.
Identification
Human beings face the identity issues a million times during their lifetime. Passports, diplomas, driver’s license, certificates, and so on help us prove our identity and abilities that we possess. We graduate from university and get a diploma. After passing a Microsoft exam, we get a certificate that proves our qualification. But what can happen if the society is overwhelmed with information? How can we differentiate what information can be trusted and what is falsified?
 When a new account is created in a social network, the system and other users identify new account as an authorized one and begin to trust it accordingly. On one hand it’s great, but on the other hand, the system can bump into serious security issues of fake information provided by the user or a third party’s identifier. Who can we trust in this case? Leader’s opinion? The Authorities? Those who establish identities?
When a new account is created in a social network, the system and other users identify new account as an authorized one and begin to trust it accordingly. On one hand it’s great, but on the other hand, the system can bump into serious security issues of fake information provided by the user or a third party’s identifier. Who can we trust in this case? Leader’s opinion? The Authorities? Those who establish identities?
Personal information is considered one of the most valuable goods nowadays. Many are stealing, trading or using the information to influence and manipulate other people. So, the question is can we really trust our information to such kinds of establishments?
As a result, Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is created to solve these exact issues and also meets all the GDPR requirements.
Self-Sovereign Identity
The main purpose of identification is to answer the question: “Who are you?” The evidence confirms the information to be true. We all know what a passport looks like. That makes it hard to forge. Self-Sovereign Identity is a new concept that provides a user with a unique independent ID. This is the way to secure your personal data according to the GDPR principals. For instance, the new digital SSI identity model stores a number of public keys and ID numbers corresponding to the concrete private data the user wants to share. The system gets rid of necessity of storing an enormous number of passwords that can be stolen, manipulated and misused.
How Exactly Do Users Control Their Data?
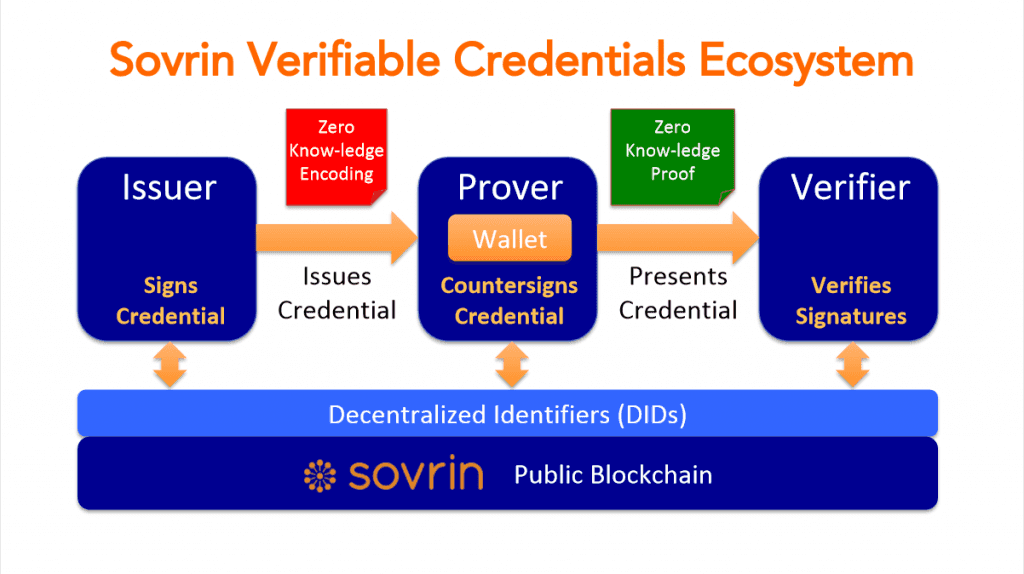
Good question. Let’s work it out. There is no data stored in the blockchain. We have only pseudonymous identifiers (DIDs), pseudonymous public keys, and agent addresses. This enables the exchange of any private data to happen entirely off-ledger. The user (a person or a company) that stores the private information spreads it in a number of entities that get their unique identification numbers.
For instance, user can keep the information about the passport and educational background in different entities. When the government institution needs some approval, whether the user is authorized for a particular service, it sends a request containing the unique identifier and the public key issued for this request. On the user’s behalf he/she receives the notification about the organization’s request containing another pair of key and identifier for disclosing the required information. If the user accepts it, the establishment is allowed to get the information needed and the user, if it’s valid, is granted with required permission. From the application user’s point of view he/she clicks on the button and receives a dialogue box with the accept/decline options. After it, the information shared or protected accordingly.
This truly puts the individual in charge of their personal data and gives him/her the control to choose who else has access to their information and how. Some of the progressive official institutions are trying to implement this new technology. For instance, e-governance in British Columbia, Canada.
10 Principles of SSI
- Existence — Users must exist independently.
- Control — Users must control their identities.
- Access — Users must have access to their own data.
- Transparency — Systems and algorithms must be transparent.
- Persistence — Identities must be long-lived.
- Portability — Information and services about identity must be transportable.
- Interoperability — Identities should be as widely usable as possible.
- Consent — Users must agree to the use of their identity.
- Minimization — Disclosure of claims must be minimized.
- Protection — The rights of users must be protected.
In short, Self-Sovereign Identity provides the best solution to the challenges of digital identification:
- Based on the open source code and standards
- Decentralized system (“Blockchain”)
- Stores private data outside the public ledger
- Selective Disclosure by default
- Pairwise-pseudonymous identifiers
- P2P network of distributed private agents
Our teams are working on the open source SSI version called Hyperledger Indy. We are developing a blockchain for distributed data and keys storage. We also share our experience by organizing meetups on this and related topics. One of the aims is to create a strong blockchain developers’ community in Voronezh.
Learn more about the new secure way of sharing private data | Sovrin Foundation | Evernym